Leuconostoc
Introduction
Leuconostocs are traditionally found in association with plant matter, fermenting vegetables, milk, dairy products, and wines and meats. Leuconostocs were first isolated in 1878 by Cienkowski. Leuconostoc usually nonpathogenic acid-tolerant organisms with optimal temperature 18 and 25°C, but the group is quite diverse. For example, L. carnosum is an anaerobic bacterium found in spoiled, packaged meat. Optimal temperature for the organism is 2°C. L. carnosum able to inhibit growth of other (even closely related) bacteria. So, it may be used as biopreservative. Leuconostoc in general is important to fermentation of vegetables.
( From MicrobeWiki )
( Further Information: Wikipedia, ScienceDirect )
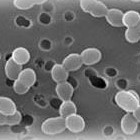
Under the microscope:
Leuconostoc

